Removing Branded IdP
Use the del-branded-idp operation to remove a branded IdP for a specific site.
Request Packet Structure
A request XML packet removing a branded IdP URL includes the del-branded-idp operation node:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
...
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>
The del-branded-idp node is presented by type SSODelRelayInput (sso.xsd), and its graphical representation is as follows:
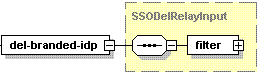
- The filter node is required. It specifies the filtering rule. For details, refer to the Available Filters section. Data type: SSODelRelayFilter (
sso.xsd).
Important: When creating request packets, put nodes and elements in the order they follow in the packet structure.
Response Packet Structure
The del-branded-idp node of the output XML packet is presented by type SSODelRelayOutput (sso.xsd) and structured as follows:
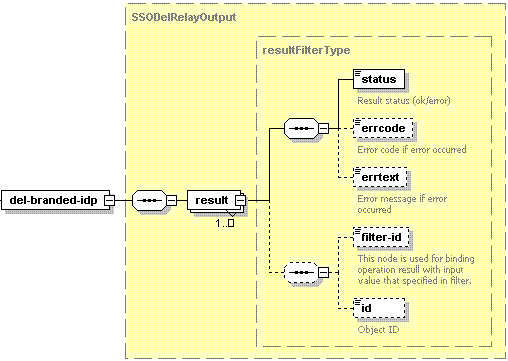
- The result node is required. It wraps the response retrieved from the server. Data type: resultFilterType (
common.xsd). - The status node is required. It specifies the execution status of the operation. Data type: string. Allowed values: ok | error.
- The errcode node is optional. It returns the error code if the operation fails. Data type: integer.
- The errtext node is optional. It returns the error message if the operation fails. Data type: string.
- The filter-id node is optional. It returns the filtering rule parameter. For details, refer to the Available Filters section. Data type: anySimple.
- The id node is optional. It returns the ID of the removed branded IdP if the operation succeeds. Data type: integer.
Samples
Removing a single branded IdP
The packet that removes branded IdP idp.example.com:1180 looks as follows:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<filter>
<idp-url>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tOjExODA=</idp-url>
</filter>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>Response:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tOjExODA=</filter-id>
<id>42</id>
</result>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>
A negative response from the server can look as follows:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<result>
<status>error</status>
<errcode>1026</errcode>
<errtext>The service is not installed.</errtext>
</result>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>
If the branded IdP was not found in Plesk database, the response from the server looks as follows:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<result>
<result>
<status>error</status>
<errcode>1013</errcode>
<errtext>Record does not exist.</errtext>
</result>
</result>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet> Removing multiple branded IdPs
The packet that removes branded IdPs idp.example.com:1180 and idp.example2.com:1180 looks as follows:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<filter>
<idp-url>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tOjExODA=</idp-url>
<idp-url>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUyLmNvbToxMTgw</idp-url>
</filter>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>Response:
<packet>
<sso>
<del-branded-idp>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tOjExODA=</filter-id>
<id>42</id>
</result>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>aWRwLmV4YW1wbGUyLmNvbToxMTgw</filter-id>
<id>32</id>
</result>
</del-branded-idp>
</sso>
</packet>