Protection Against Brute Force Attacks (Fail2Ban)
IP address banning (Fail2Ban) is an automated way to protect your server from brute force attacks. Fail2Ban uses regular expressions to monitor log files for patterns corresponding to authentication failures, seeking for exploits, and other entries that can be considered suspicious. Such log entries are counted, and, when their number reaches some predefined value, Fail2Ban either sends a notification email or bans the attacker’s IP for a pre-defined length of time. When the ban period is over, the IP address is automatically unbanned.
Fail2Ban logic is determined by a number of jails. A jail is a set of rules covering an individual scenario. The settings of the jail determine what is to be done once an attack is detected according to a predefined filter (a set of one or more regular expressions for monitoring the logs). For more information, see Fail2Ban Jails Management.
Note: To use Fail2Ban, administrators who upgrade from Plesk 11.5 must obtain a new Plesk Onyx license key either directly from Plesk or from their vendor.
To set up Plesk to automatically ban IP addresses and networks that generate malicious traffic:
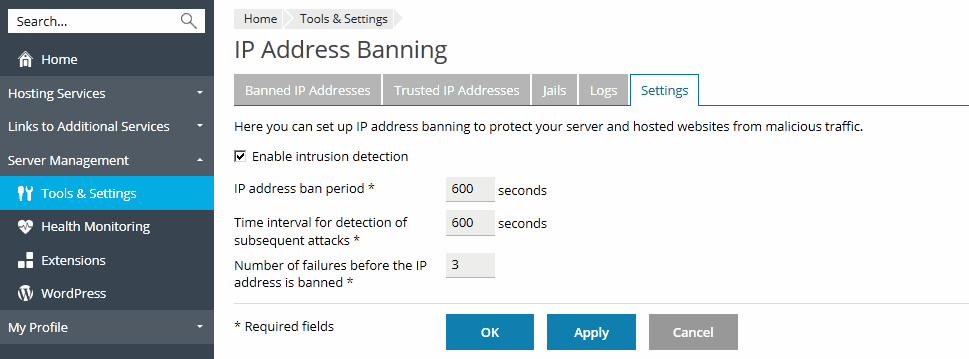
- Go to Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning (Fail2Ban) (in the Security group). The Fail2Ban component has to be installed on your server.
- Select the Enable intrusion detection checkbox. This will activate the Fail2Ban service.
- Specify the following settings:
- IP address ban period – the time interval in seconds for which an IP address is banned. When this period is over, the IP address is automatically unbanned.
- Time interval for detection of subsequent attacks - the time interval in seconds during which the system counts the number of unsuccessful login attempts and other unwanted actions from an IP address.
- Number of failures before the IP address is banned – the number of failed login attempts from the IP address.
- Click OK.
Now all active Fail2Ban jails will be used to monitor the log files and to ban suspicious IP addresses.
Fail2Ban in Plesk has the following limitations and peculiarities:
- Fail2Ban does not provide protection against attackers with an IPv6 address. Fail2ban in Plesk relies solely on IPs (without hostname lookups) unless reconfigured.
- Fail2Ban cannot protect from distributed brute force attacks, since it identifies intruders by their IP address.
- If you have your Plesk installed on a VPS, the VPS iptables records
limit (
numiptent) might affect the work of Fail2Ban. When this limit is exceeded, Fail2Ban will stop working properly and in the Fail2Ban log you will find a line such as:fail2ban.actions.action: ERROR iptables -I fail2ban-plesk-proftpd 1 -s 12.34.56.78 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable returned 100In this case, contact your VPS hosting provider to solve the issue. - If you had Fail2Ban installed on your server before upgrading to Plesk Onyx, the package will be replaced by Plesk’s Fail2Ban package. If your already installed package is newer than the one provided with Plesk, the upgrade might fail. Existing jails will not be overwritten and you can manage them in Plesk together with Plesk Onyx jails.
If an IP address should not be blocked:
- Go to Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning (Fail2Ban) > Trusted IP Addresses > Add Trusted IP.
- In the IP address field, provide an IP address, an IP range, or a DNS host name, and click OK.
You can view and download Fail2Ban log files in Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning (Fail2Ban) > the Logs tab.
You can view the list of banned IP addresses, unban them, or move them to the list of trusted addresses in Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning (Fail2Ban) > the Banned IP Addresses tab.
You can view the list of IP addresses that will never be banned, add IP addresses to and remove from this list in Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning (Fail2Ban) > the Trusted IP Addresses tab.