Deleting Database Users
You can remove user accounts from a certain database. Specify the user login name and ID of the database where you want to remove the user. You can remove all users from all databases in a single del-db-user operation.
Request Packet Structure
A request XML packet deleting a user from the database includes the del-db-user operation node:
<packet>
<database>
<del-db-user>
...
</del-db-user>
</database>
</packet>
The del-db-user node is presented by type
DatabaseDelDBUserInputType (database_input.xsd), and its graphical
representation is as follows:
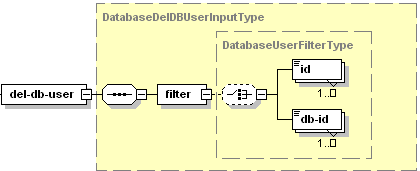
Note: The interactive schema navigator for all request packets is available here: http://plesk.github.io/api-schemas/1.6.9.1/agent_input.svg.
- The filter node is required. Specifies the filtering rule. For more information, refer to the Available Filters section. Data type: DatabaseUserFilterType.
- The id node is optional. It specifies the ID of the user you want to delete. Data type: integer.
- The db-id node is optional. It specifies the ID of the database where a new user will be created. Data type: integer.
Remarks
You can delete multiple users from the database using a single packet. Add as many del-db-user operations as the number of different users you want to delete from the database.
<database>
<del-db-user>
...
</del-db-user>
...
<del-db-user>
...
</add-db-user>
</database>
You can also delete all users from the different databases using this construction.
Note: Use the <filter/> parameter if you want to delete all users from all databases available for the sender.
Note: When creating request packets, put nodes and elements in the order they follow in the packet structure.
Response Packet Structure
The del-db-user node of the output XML packet is presented by type
DatabaseDelDBUserOutputType (database_output.xsd) and structured
as follows:
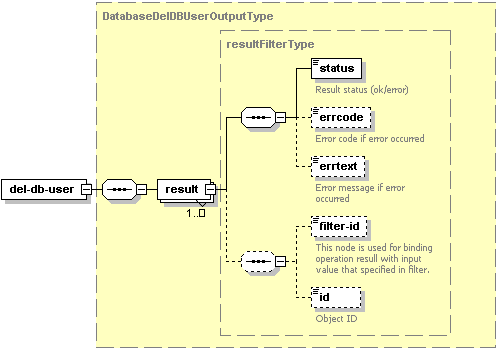
Note: The interactive schema navigator for all response packets is available here: http://plesk.github.io/api-schemas/1.6.9.1/agent_output.svg.
- The result node is required. It wraps the response retrieved
from the server. Data type: resultFilterType (
common.xsd). - The status node is required. It specifies the execution status of the del-db-user operation. Data type: string. Allowed values: ok | error.
- The errcode node is optional. It returns the error code if the del-db–user operation fails. Data type: integer.
- The errtext node is optional. It returns the error message if the del-db–user operation fails. Data type: string.
- The filter-id node is optional. It returns the filtering rule parameter. For more information, refer to the Available Filters section.
- The id node is required. If the del-db-user operation succeeds, it specifies the database user ID. Data type: integer.
Deleting database user
This request packet removes the user with ID 55 from the database with ID 2.
<packet>
<database>
<del-db-user>
<filter>
<id>55</id>
</filter>
</del-db-user>
</database>
</packet>
Reponse:
<packet>
<database>
<del-db-user>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>55</filter-id>
<id>55</id>
</result>
</del-db-user>
</database>
</packet>
Deleting multiple database users
This request packet removes all users from the database with ID 45.
<packet>
<database>
<del-db-user>
<id>45</id>
</del-db-user>
</database>
</packet>
Respone (when the users with ID 7 and ID 8 were removed from the database):
<packet>
<database>
<del-db-user>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>45</filter-id>
<id>7</id>
</result>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<filter-id>45</filter-id>
<id>8</id>
</result>
</del-db-user>
</database>
</packet>