Creating a Service Plan
Use the add operation to create plans. When creating a plan, it is enough to specify a plan name. If you are authorized as the Administrator but want to add a plan to a reseller’s plan list, specify the reseller ID or username. Additionally, you can specify plan settings when creating a plan.
Request Packet Structure
A request XML packet adding a new service plan to Plesk database includes the add operation node:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
...
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
The add node is presented by type DomainTemplateAddInputType
(domain_template.xsd). Its graphical representation is as follows:
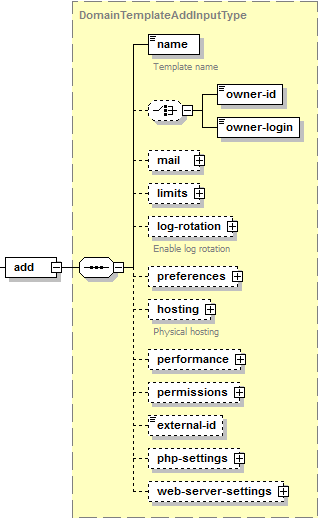
- The name node is required. It specifies the name of the service plan. Data type: string.
- The owner-id node is optional. It specifies the ID of the service plan owner. Data type: integer.
- The owner-login node is optional. It specifies the login name of the service plan owner. Data type: string.
- The mail node is optional. It specifies a collection of email
preferences that will be assigned to a new subscription created using
this plan. Data type: MailPreferences (
plesk_mailname.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Mailing settings section. - The limits node is optional. It specifies a collection of
limits that will be set for new subscriptions created using this
plan. Data type: domainLimits (
plesk_domain.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Limits section. - The log-rotation node is optional. It is used to turn on/off
rotation of log files related to a subscription created using this
plan. Data type: LogRotationType (
domain_template.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Log Rotation Settings section. - The preferences node is optional. It is used to specify a
collection of preferences for new subscriptions created using this
plan. Data type: DomainTemplatePreferecesType
(
domain_template.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Preferences section. - The hosting node is optional. Specifies physical hosting
settings for new subscriptions created using this plan. Data type:
DomainTemplatePHostingPreferences (
domain_template.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Hosting Settings section. - The performance node is optional. It specifies performance
settings for new subscriptions created using this service plan. Data
type: DomainPerformanceType (
plesk_domain.xsd). See the structure of this node in the Performance Settings section. - The permissions node is optional. It defines which services and privileges that can be enabled in a service plan. Data type: none. See the structure of this node in the Permissions section.
- The external-id node is optional. It defines a service plan identifier in the Plesk components (for example, Business Manager). Data type: sting.
- The php-settings node is optional. It specifies custom PHP
settings that will act as a preset for all plan subscriptions. Data
type: phpSettings (
domain_template.xsd). See the section PHP Settings for details. - The web-server-settings node is optional. It specifies custom
web server settings that will act as a preset for all plan
subscriptions. Data type: webServerSettings
(
domain_template.xsd). See the section Web Server Settings for details.
Note: When creating request packets, put nodes and elements in the order they follow in the packet structure.
Note: The interactive schema navigator for all request packets is available here: http://plesk.github.io/api-schemas/1.6.9.1/agent_input.svg.
Response Packet Structure
The add node of the output XML packet is of type
DomainTemplateAddOutputType (domain_template.xsd) which has the
following presentation:
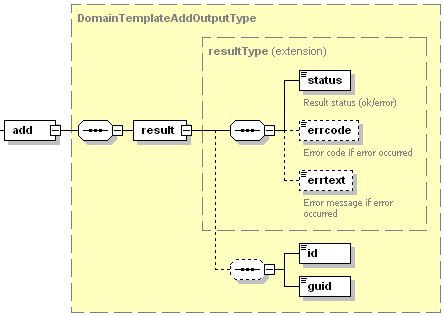
- The result node is required. It wraps the response got from the
server. Data type: resultType (
common.xsd). - The status node is required. Specifies the execution status of the operation. Data type: string. Allowed values: ok | error.
- The errcode node is optional. Returns the error code when the operation fails. Data type: unsignedInt.
- The errtext node is optional. Returns the error message if the operation fails. Data type: string.
- The id node is optional. It is required if the operation has succeeded. Returns the unique identifier of a service plan just added to the Panel. Data type: integer.
- The guid node is optional. Returns the GUID of a service plan just added to the Panel. Data type: string.
Note: The interactive schema navigator for all response packets is available here: http://plesk.github.io/api-schemas/1.6.9.1/agent_output.svg.
Creating service plans for different Plesk users
To create a plan on behalf of the reseller with ID 12, issue the following packet.
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan</name>
<owner-id>1</owner-id>
<mail>
<mailservice>1</mailservice>
</mail>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Response:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<id>11</id>
<guid>15b56488-60f7-1b15-b489-09ece02dbb4f</guid>
</result>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
When creating a service plan for Plesk Administrator, omit the reseller identifiers:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan</name>
<mail>
<webmail>roundcube</webmail>
</mail>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Creating multiple service plans
To create two service plans with a single packet, include two different add blocks:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan1</name>
<mail>
<webmail>none</webmail>
</mail>
</add>
<add>
<name>quick_plan1</name>
<mail>
</mail>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Response:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<id>12</id>
<guid>acd360bc-6c23-2689-76e5-b01438f5e4a3</guid>
</result>
</add>
<add>
<result>
<status>ok</status>
<id>13</id>
<guid>27fc6501-c137-49cd-5c36-eb74954e68a2</guid>
</result>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Mailing settings
The following packet creates a service plan and configures its mail settings.
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>bounce_template</name>
<mail>
<nonexistent-user>
<bounce>Email address does not exist.</bounce>
</nonexistent-user>
<webmail>true</webmail>
</mail>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Log rotation
To disable log rotation for plan base_plan, use the following packet:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan</name>
<log-rotation>
<off/>
</log-rotation>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
The following packet creates a service plan that enables log rotation that allows to store up to 30 handled log files per subscription, and removes active log once a week:
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan</name>
<log-rotation>
<on>
<log-condition>
<log-bytime>Weekly</log-bytime>
</log-condition>
<log-max-num-files>30</log-max-num-files>
<log-compress>true</log-compress>
</on>
</log-rotation>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>
Preferences
The following packet creates a service plan with specific preferences.
<packet>
<service-plan>
<add>
<name>base_plan</name>
<preferences>
<stat>6</stat>
<maillists>true</maillists>
<dns_zone_type>master</dns_zone_type>
</preferences>
</add>
</service-plan>
</packet>